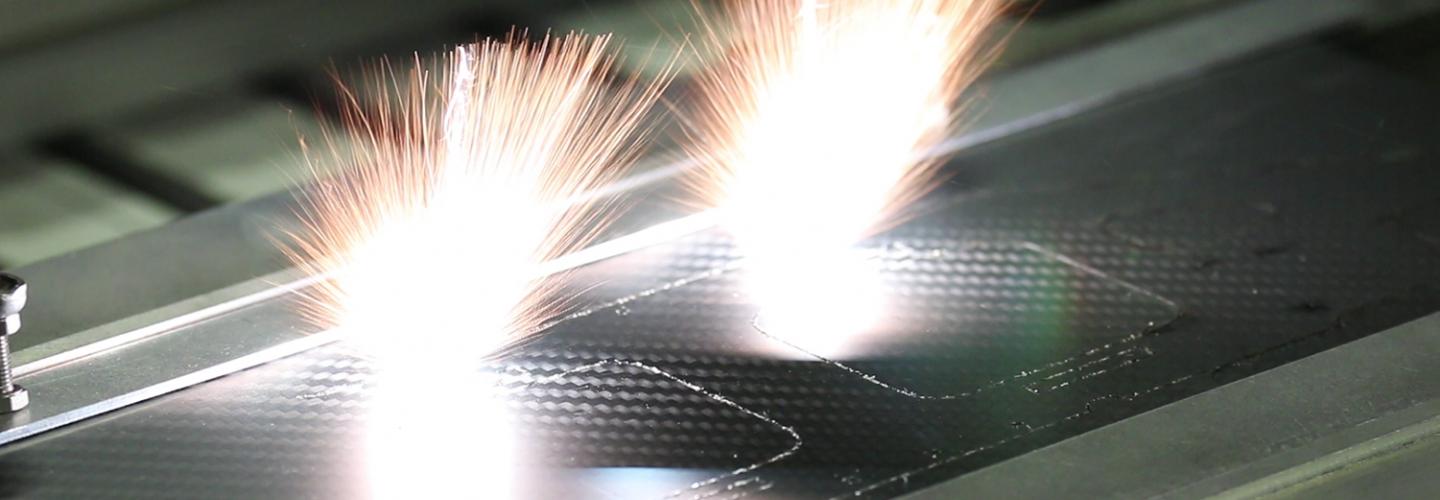
Laser Cutting
As a wear-free cutting tool, lasers quickly established their place in industrial manufacturing. In conjunction with a scan system, they offer compelling advantages such as high flexibility in shaping cutter contours, low set-up costs and high process speeds (and hence shorter process times). Unlike traditional mechanical cutting methods, the laser cutting process can be applied to a wide range of materials, from films and paper all the way to glass and metals.
Different lasers emitting in a wide range from UV to IR are integrated in laser cutting processes.
SCANLAB can offer a large variety of mirror coatings for every need. Please contact our sales team even if your specific application is not among to following examples.
CO2 Cutting Processes
Paper, Cardboard and Wood
Cutting applications are mainly characterized by large fields, small spots, high throughput and on-the-fly processing. In label cutting (e.g. kiss cuts), contours are only cut into the upper material layer, without damaging the layers below. The key requirements for package manufacturing (e.g. cartons) are design flexibility and high contour-precision to ensure mechanical functionality, followed by rapid processing of large quantities. In the manufacture of grinding discs, one major contactless laser cutting advantage is that it is a wear-free cutting tool.
Technical Textiles, Fabrics and Leather
High flexibility means waste minimization, free-form cutting and cost-effective manufacturing, even with the smallest production runs.
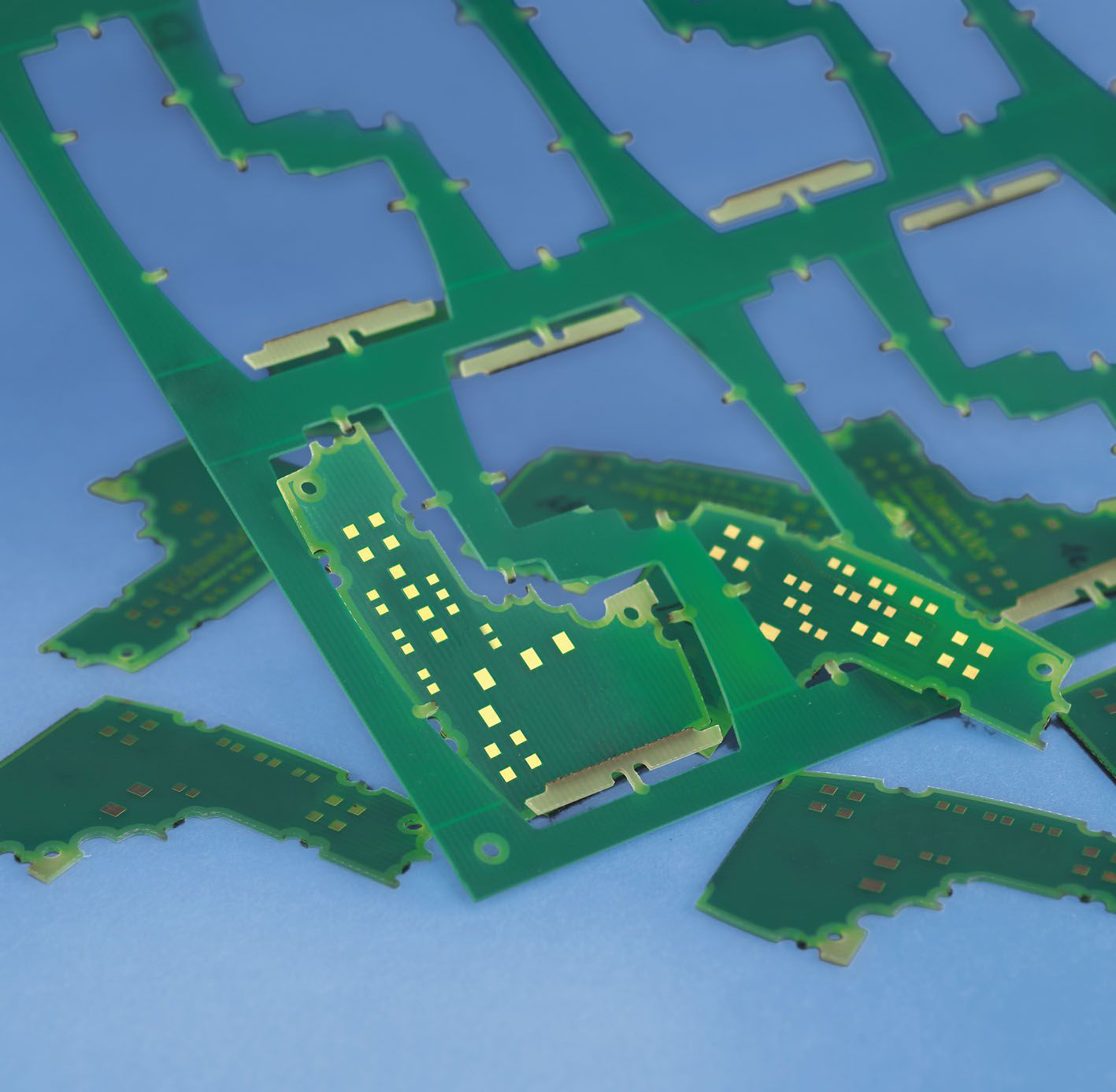
Plastics and Films
Advantages of laser cutting plastics and films include freedom from having to secure materials (as the process is force-free) and clean cuts that don't require post processing. Of course speed, precision and cost-efficiency are further success factors.
Fiber- und YAG Cutting Processes
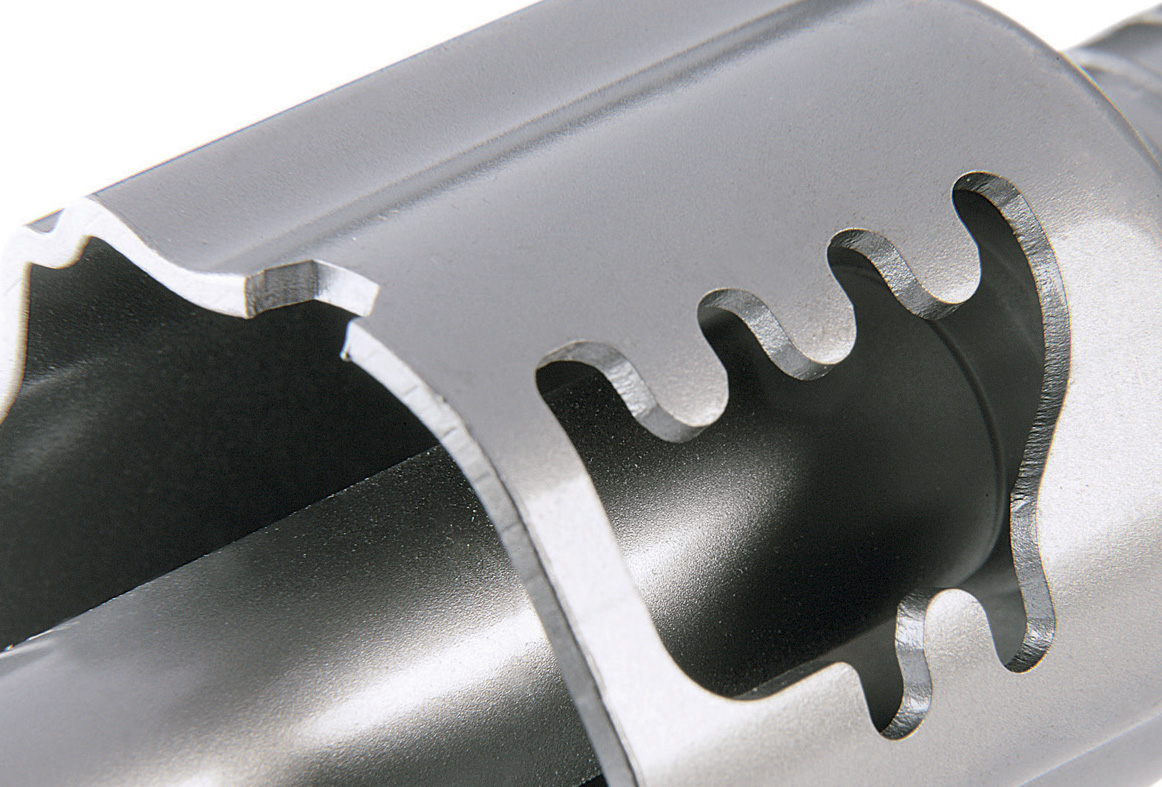
Glass and Ceramics
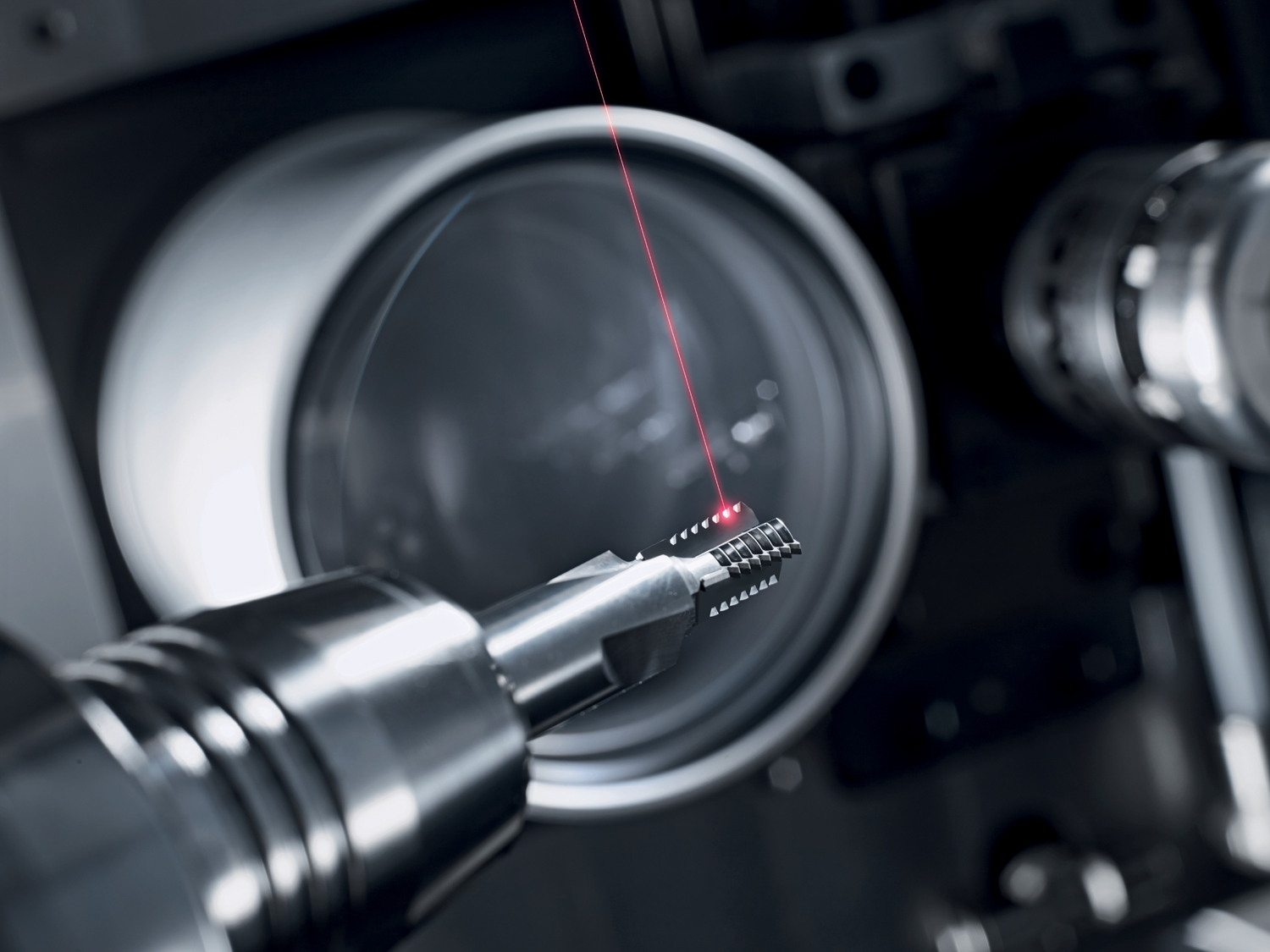
Due to clean cut edges, high precision and freedom from wear, it is no wonder scan systems are so widely used to cut glass and ceramics. In conjunction with USP lasers, an effective and simultaneous processing is possible. The pre-defined contours are scanned quickly, often and with high repeat accuracy, without significantly thermal input into the material. Microcutting is typically used for hardened glass, diamond, sapphire glass (corundum), gorilla glass or ceramics.

Metals
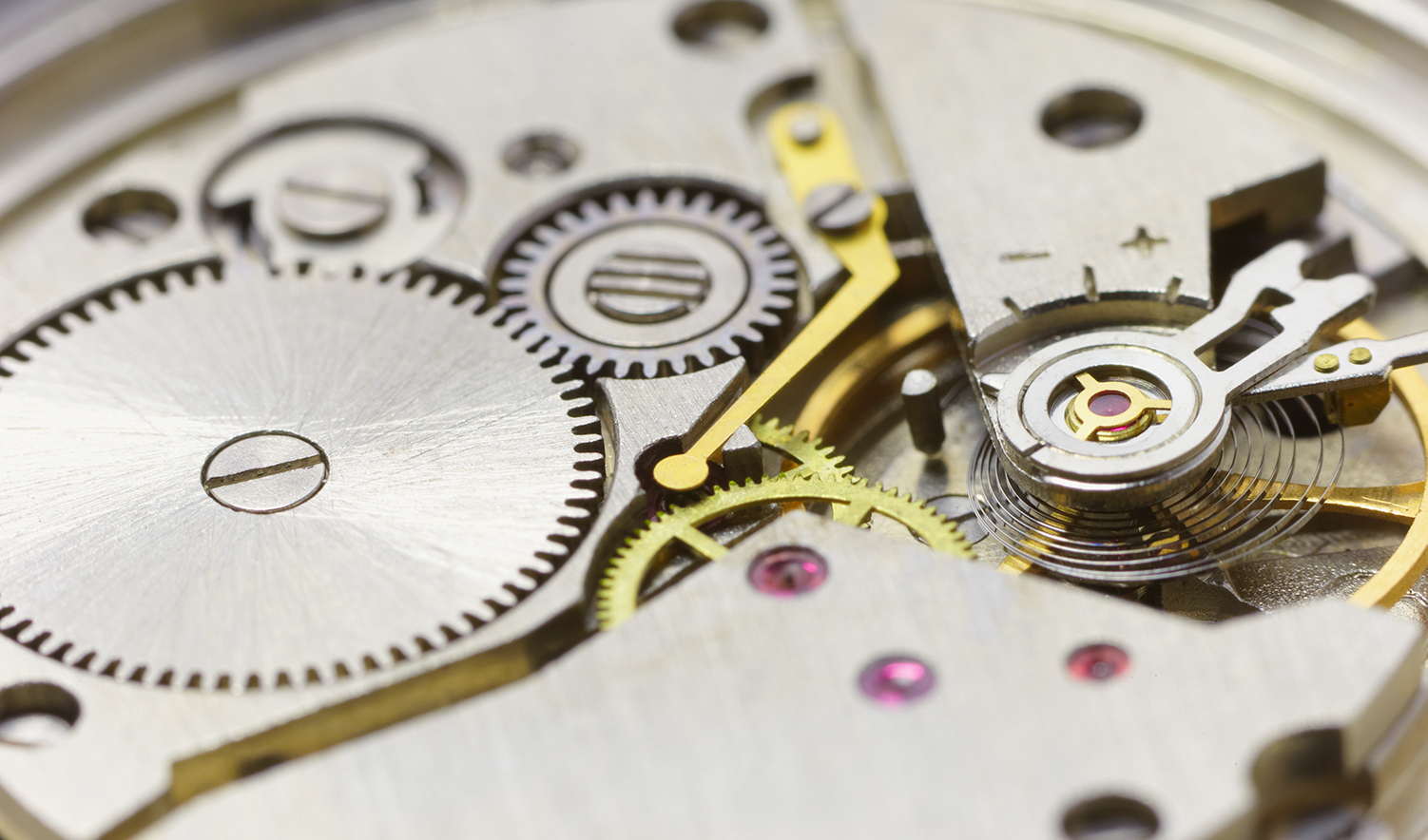
In combination with scan systems, lasers offer many advantages for microcutting of metal. The low material disruption of the process allows fabrication of ultra-fine parts such as time-piece pointers and gears.

Suitable Solutions
CO2 Lasers
- powerSCAN II (processing of large image fields)
- intelliSCAN
- laserDESK
Other Lasers
Laser Applications Freely Cross Industrial Boundaries
Laser processing methods are employed in numerous industries. Click a specific industry link to see a selection of processing methods that use galvanometer scanners.