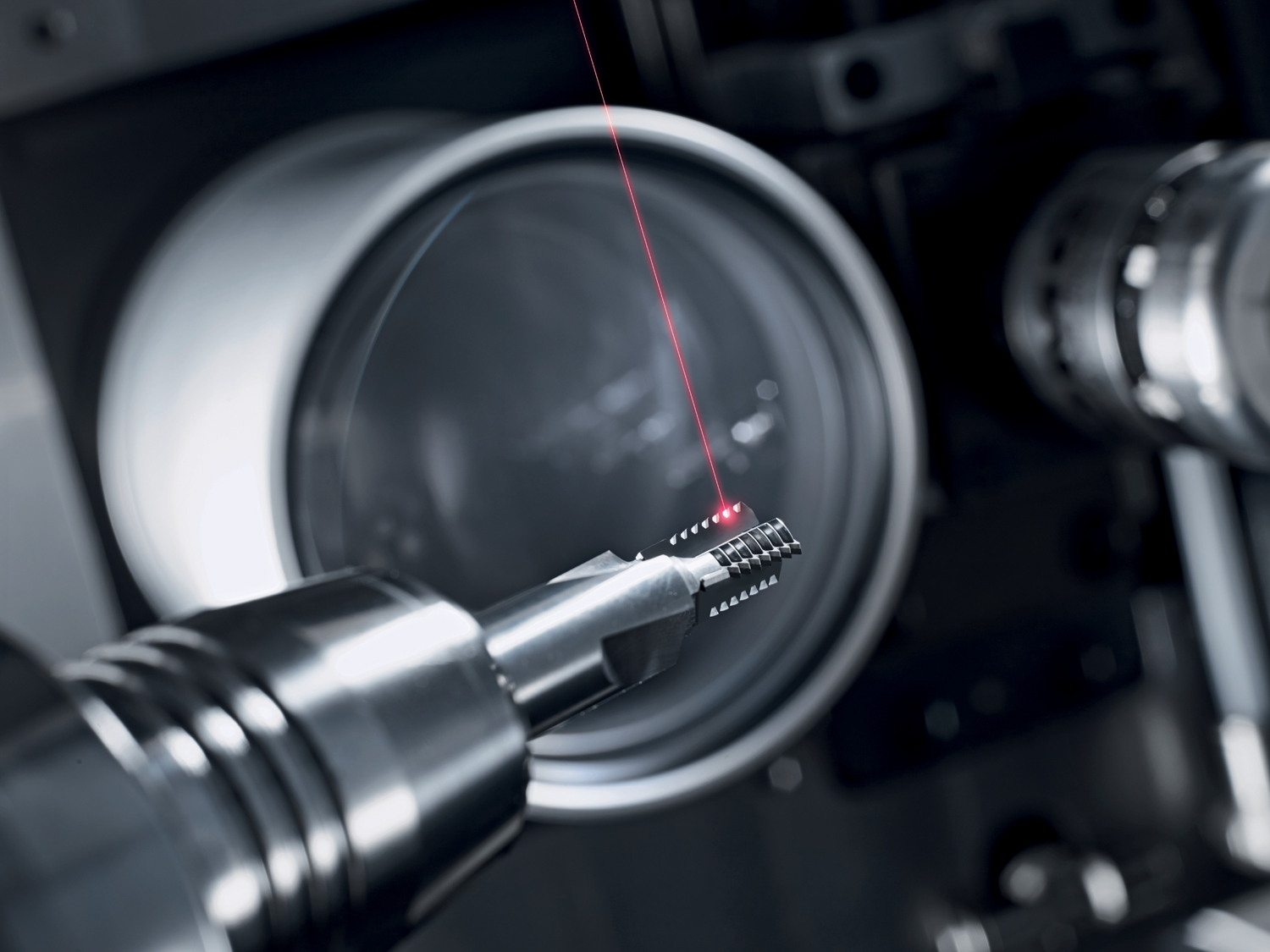
Laser Drilling
Laser drilling outshines traditional methods such as electric discharge machining (EDM), electrochemical machining (ECM) or mechanical drilling in many aspects.
- Highly flexible
- Contact-free and wear-free
- Highly precise and extremely fast
- Minimal heat input
- Process medium (gas) as option
- Tiny diameters and high aspect ratios achievable
Lasers can remove nearly any kind of solid material (e.g. hardened steel, hard metal, ceramics and composites) regardless of material properties (e.g. electrical conductivity, hardness). As the removal method is contactless and force-free, even sensitive materials such as glass and thin polymer film can be processed with low defects.
The application of scan systems for laser drilling offers not only outstanding flexibility and automation capabilities, but also great potential for miniaturization due to adjustable spot sizes down to mere micrometers. Ultra-fine bore holes in the sub-millimeter range (e.g. trepanning for diameters ≥ 40 µm with high aspect ratios, or percussion drilling for diameters ≥ 20 µm) with very sharp edges at bore entrance/exit holes and short process times are readily achievable.
Laser Perforating
Lasers have found widespread use in the packaging industry for perforation applications, ranging all the way from fine holes for gas exchange in freshness-packaging to tearing aids and more. Here, scan systems provide flexibility needed for diverse structures and designs, as well as the dynamics necessary for high-volume manufacturing.
Microdrilling
Micro-Vias play a very important role for highly integrated circuits on printed circuit boards (PCBs). HDI PCBs in particular enable a very high circuit density. For via hole drilling (VHD), the laser is the ideal tool for creating fine holes precisely and with very high throughput. The intelliDRILLse II, which has been specially optimized for this application, enables cost-efficient production thanks to short jump times and maximum precision.
5-axis Micromachining
Optimized scanning solutions like the precSYS 5-axis micromachining system are capable of drilling injection nozzles, which require precise holes in the sub-millimeter range with freely-definable geometries and high aspect ratios. An additional and very new application is the laser drilling of guide plates for advanced vertical probe cards in the electronic industry.
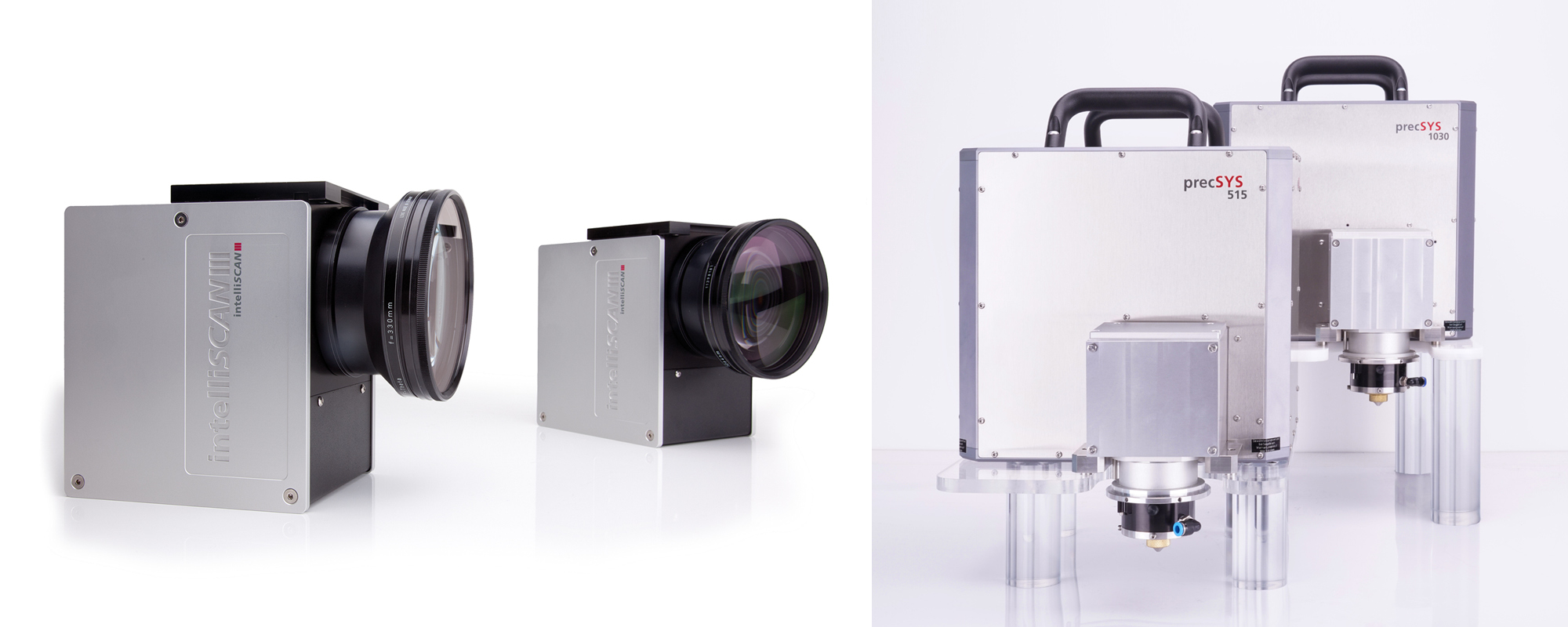

High Performance Scan Systems
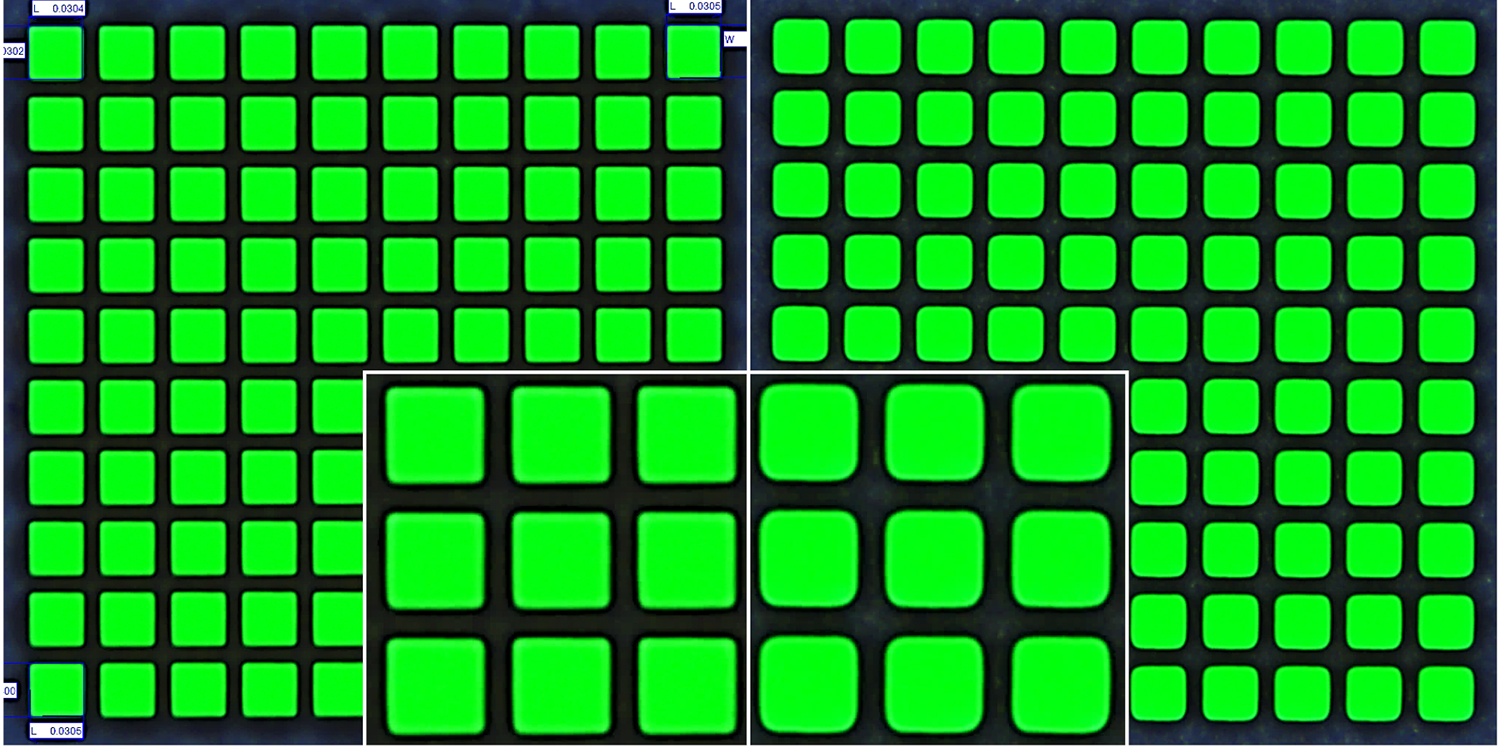
Entry side of square holes with 30 μm edge lengths in a 250 μm thick Si3N4 ceramic substrate, made using a 515 nm laser (left), and a 1.030 nm laser (right) precSYS system (Courtesy: Posalux)
Laser Applications Freely Cross Industrial Boundaries
Laser processing methods are employed in numerous industries. Click a specific industry link to see a selection of processing methods that use galvanometer scanners.